Bloodborne Pathogens and Needlestick Injury
7/2/2019
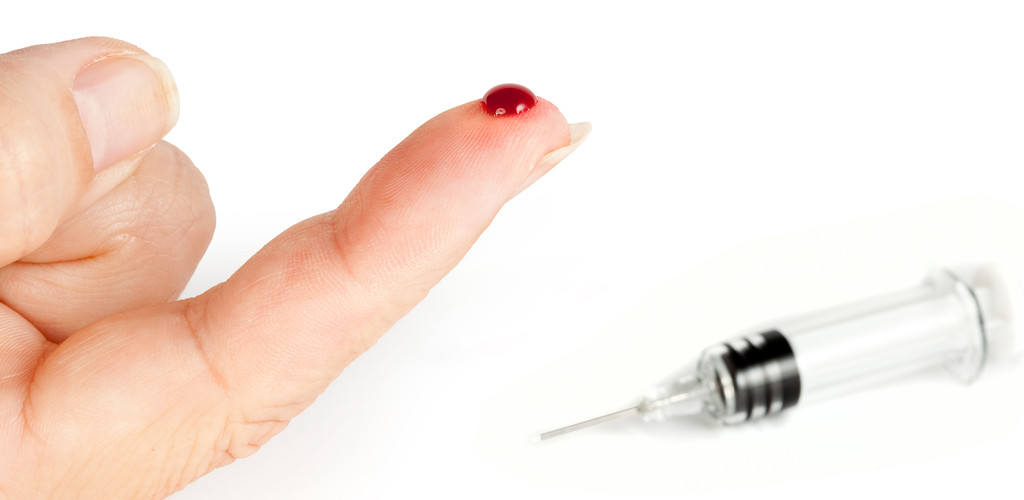
What Are They?
Bloodborne pathogens are microorganisms found in blood that can cause disease in humans.
Common Bloodborne Pathogens
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- HIV
Who is Most at Risk?
- Healthcare workers
- First responders
- Housekeeping staff
- Nurses
- Doctors
Prevention
Bloodborne pathogens are often transmitted to workers via a needlestick injury. This may occur when the worker is handling medical waste, drawing blood from a patient, or putting up an intravenous line.
Employers need to have an exposure control plan in place to reduce occupational exposure risk. The plan needs to detail how employees will be protected, for example, by the mandatory wearing of gloves. Education and training play a large role in prevention too. Vaccinations for hepatitis B can be given to all exposed employees. Engineering controls can largely eliminate the exposure of workers to bloodborne pathogens. For instance, the use of shielded needles and plastic capillary tubing.
First Aid for Needlestick Injury
If a worker is pierced by any sharp object that’s contaminated with blood or other infectious material, action should be taken immediately.
- Flood the injured part with running water
- Wash with soap or suitable disinfectant
- Seek medical help
- Report the incident to the employer as soon as possible
